Digitized Telephone services
In the past, we had manual exchanges which involved a great task in switching and routing of calls to various subscribers that increased network traffic and longer setup times. Also fault checking and identification was very difficult.
Now, with the introduction of electronic exchanges which uses a stored program concept for switching of calls and automatic error checking, the manual tasks involved in such operations has reduced, network traffic has reduced and call setup time has reduced. We have transformed from the stream of electronic exchanges to digital exchanges which used PCM (pulse code modulation) techniques to transmit speech signals in the digital form between two digital exchanges. Such digital exchanges provides multiplexed speech channels, latest fiber optic/FIOS technologies for signal transmission, reduced network traffic, least call setup time, better error checking and control and better customer support.
An example for a digital exchange is the E-10B model exchange. The organization of an E-10 B exchange is as shown below –
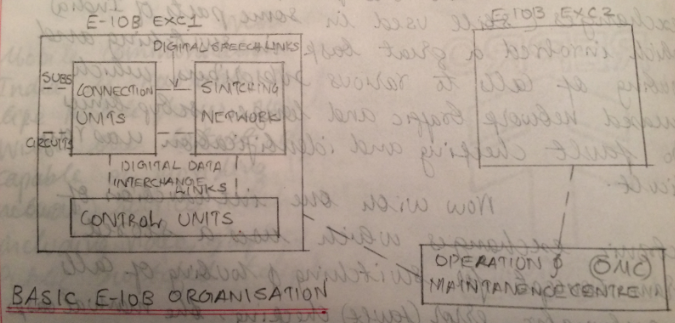
The main features of E-10B digital exchange are as follows –
a) Stored program control (SPC)
b) Time division multiplexing (TDM)
c) Use of Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)
d) Separation of switching functions from exchange management functions
e) Distributed common control structure for switching using functionality dedicated control units
f) Centralized management of E-10B exchanges through the operation and management center (OMC)
g)Could be used of implementing subscriber exchanges, Tandem/Tax exchanges (Transit exchanges) and Hybrid exchanges combining qualities of subscriber and transit exchanges.
h) Supports more subscribers and provide better customer support by detailed billing, alarm calls, identification of malicious calls and hot-line facilities.
I) Having a modular architecture, E-10B exchanges could be expanded to meet increased demand by mere insertion of hardware equipment.